Cost overruns are extraordinarily common in every single sector of performance, every industry, and every part of the world. They can reach enormous magnitudes in both short-term and long-term projects, seriously damaging their financial health and reducing chances for success.
Nevertheless, a comprehensive and systematic approach to cost management is a definite remedy to this problem. It serves to align project needs with available resources, supervise current and future expenses, and analyze cost performance. Thus, it can assist you in avoiding the risk of cost overrun a great deal.
In this article, we will define what project cost management is, discuss its role in project planning, and overview its major components to help you see why you must invest in cost management yourself.
What Is Project Cost Management?
“Cost Management is a function which includes the processes that are required to maintain effective financial control of projects (evaluating, estimating, budgeting, monitoring, analyzing, forecasting and reporting the cost information).” – PMI
It aims to:
- Calculate how much money is needed to perform tasks and duties involved in the project.
- Develop a project budget and allocate funds as per the results of cost estimation.
- Track down how much is spent on project-related activities and encourage compliance with the created budget.
- Gather statistical data regarding actual project expenses to inform future decision-making.
When all these objectives are achieved, you will take project costs under control, reduce the risk of loss, and maximize profit.
Role of Cost Management in Project Management
Cost management is an integral part of project management in general, and its contribution to the project’s success is more than vital. To understand why, let’s identify the primary purpose of project management and explore the issue of project constraints in some detail.
Project Planning and the Triple Constraint
As such, the primary strive of project management is to attain formulated project goals within a specific timeframe, scope, and budget. These three restrictive parameters are illustrated within the Triple Constraint Model as interdependent: a change in one of them inevitably entails changes in two others.
For instance, when the project’s scope is enlarged, the number of efforts and resources needed to complete it increases. As a result, the deadline and the cost of that project become altered as well.
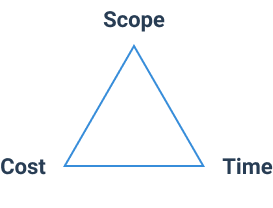
In the present-day world of business, it is particularly important to remember the interdependence among project scope, timeframes, and costs. The modern environment is rapidly evolving and extremely competitive. It makes managers compromise at every step and choose between affordability and quality, speed and effectiveness, stakeholder satisfaction, and profitability. The list goes on.
Thus, you must always be aware of the fact that a decision to complete the project in a shorter term will entail the necessity to reduce the volume of project-related tasks or invest more money in skilled personnel and technology. Otherwise, you will likely fail to meet the deadline or the quality of your work will badly suffer.
Overall, the Triple Constraint Model is here to remind you of that.
Why Cost Planning Is Especially Important?
Statistical data shows that cost is the most critical factor in defining project failures and success:
- According to the McKinsey-Oxford study on performance in the IT sector, cost overruns in software projects can reach 66% on average, and in projects that are not related to software – 43%.
- However, IT companies are not the only ones to bear financial risks after going over their project budgets. A recent review of evidence from international construction industries revealed that an average cost overrun in medium-sized projects is as high as 32.5%, whereas in megaprojects, the number may reach 88%.
These statistics indicate that regardless of all the advancements in the practice and theory of project cost management throughout the last decades, many projects still suffer the consequences of inadequate expenditure prediction and control.
Partially, project cost overruns may be attributed to the lack of a clear strategic plan and managers’ inability to consider potential risks and environmental changes. However, cost underestimation can be validly named the leading reason why businesses go far above their budgeted expectations.
So, unlike a thoughtless attitude to cost management, a serious and careful approach to this essential practice can take you and your project a long way.
4 Key Project Cost Management Processes
The process of successful project cost management is conducted systematically and usually involves 4 steps:
- Work scope planning
- Cost estimation
- Budgeting
- Spending control
In this section, we will overview each of them separately and identify their main outcomes/values.
Work Scope Planning
To comprehend how much money is required to deliver a project, you must know it from the inside out: its short-term objectives, long-term goals, and the environment where it is going to be realized. In other words, you need an evidence-based and thorough plan.
Here’s why:
“Many projects fail either because they bite off more than they can chew and thus grossly underestimate time and money or because a significant part of the work has been overlooked. One tool that can help you avoid these problems is the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), which aids in the process of determining scope and tasks and developing estimates.” – HBR
A WBS is essentially a hierarchical diagram of all the things you should accomplish within a project. It starts with major milestones or project phases at the top of the diagram and ends with smaller work packages, e.g., the groups of tasks that must be done to attain the desired deliverables.
For example, a WBS for a content marketing project could look something like this:
In this WBS diagram, major project activities are highlighted in blue, mid-level deliverables are highlighted in red, and orange blocks designate work packages.
As a result of representing your entire work scope in such a visual format, you get aclear picture of the activities involved in the project. Then, you can use the WBS to evaluate which resources you need, how many of them you already have, and how much you still must acquire. After that, you may proceed toward a more detailed estimation of project-related expenses.
Get a free WBS template here. 👈
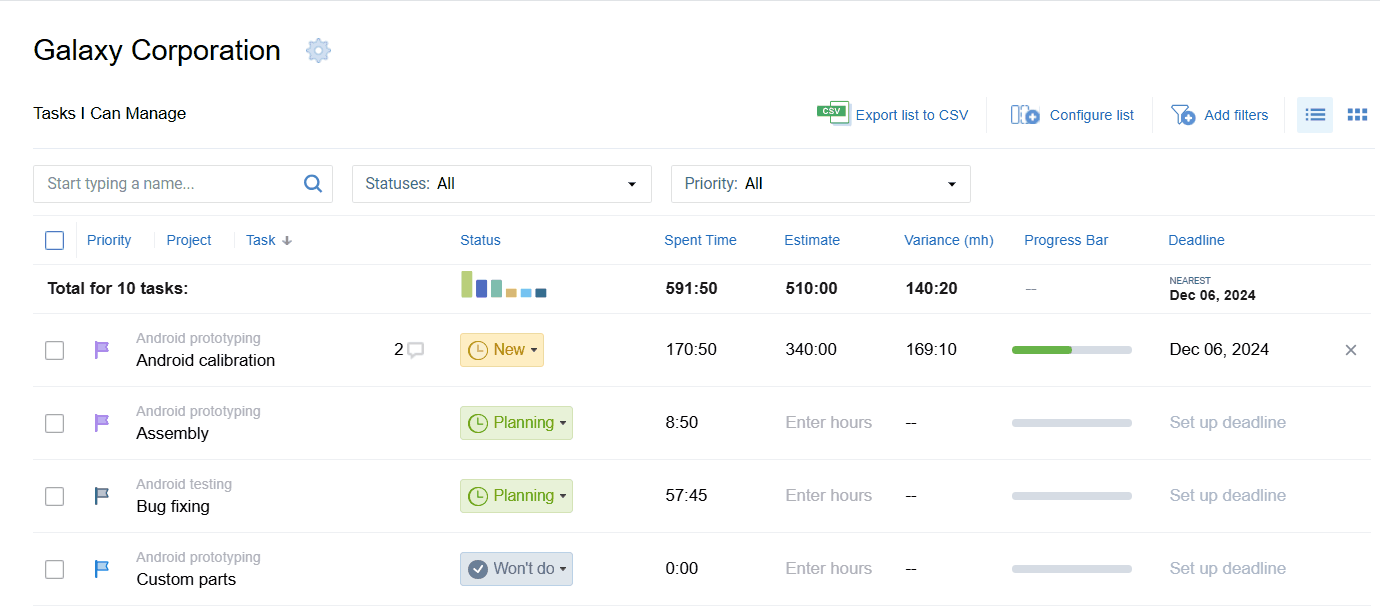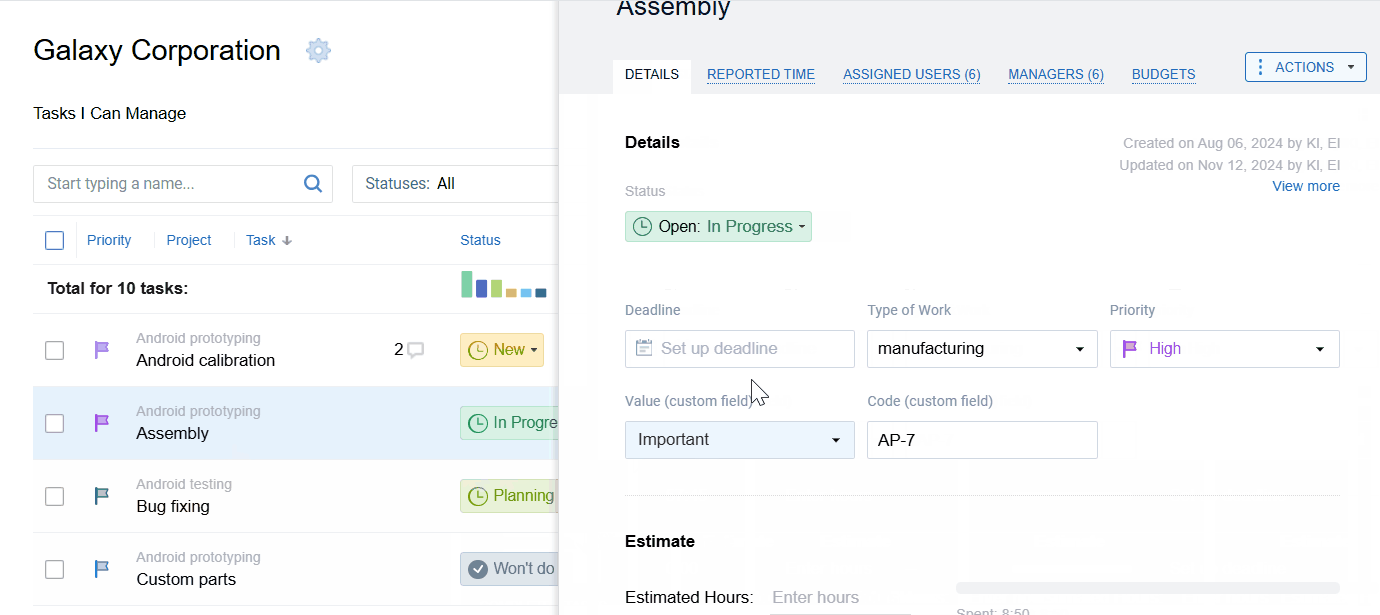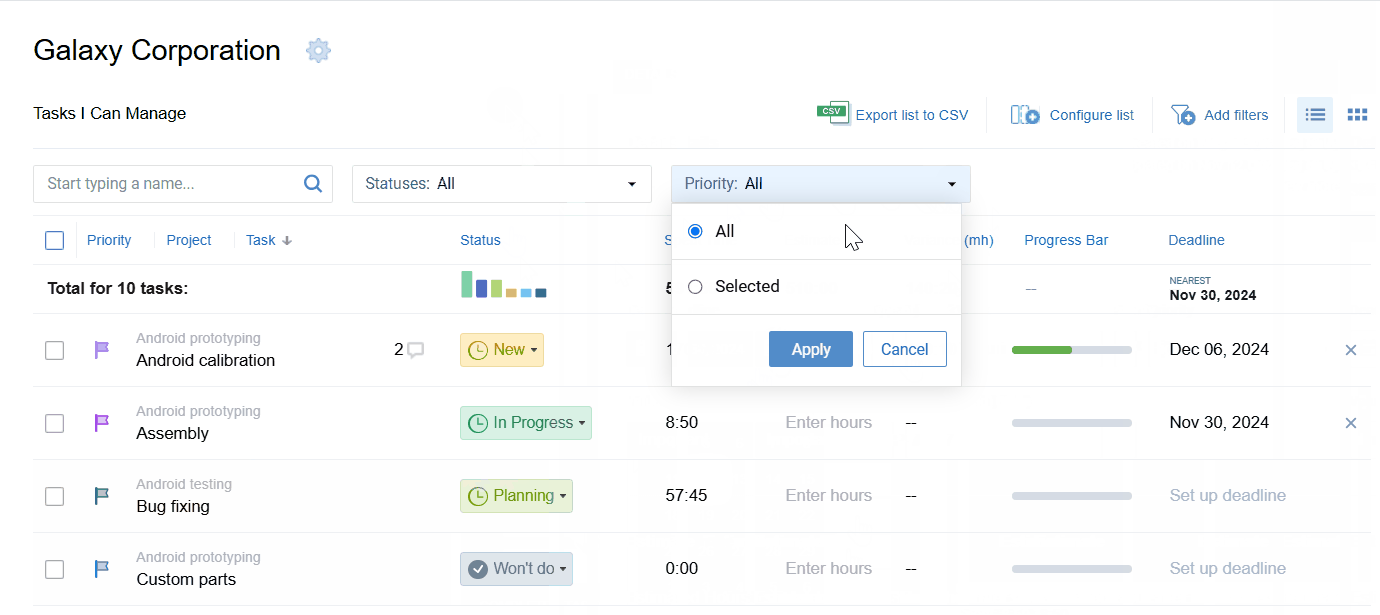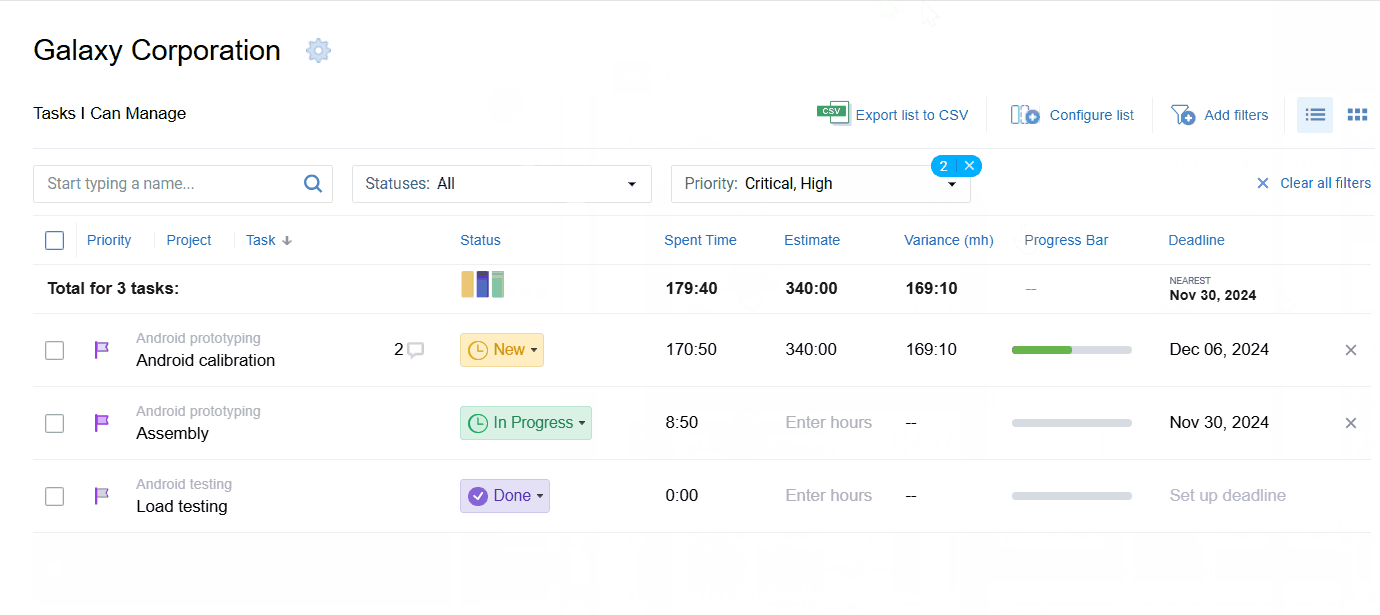
Use actiTIME to plan out your project scope the easy way: create as many tasks as you want, set deadlines and priorities, allocate work to employees, and then track their performance via a variety of visual progress tools.
Cost Estimation
” Cost Estimating is the process of assembling and predicting the costs of a project. It encompasses the economic evaluation, project investments cost and predicting or forecasting of future trends and costs.” – PMI
Let’s break down the three elements of cost estimation one by one:
Economic evaluation is meant to give you an idea of whether your project is financially and technically feasible. It’s carried out at the initial planning stage so where you produce rough estimates of project expenses and potential profits.
Project investment cost implies more accurate cost estimation. That’s the phase where you define your budget and develop a more precise picture of the majority of expenses your project will incur (at lease at the start of its life cycle).
You can use your WBS (and resource breakdown structure) to sort out project costs: since you already know what you need to do and what type of resources are required, the primary task here is to identify their prices as accurately as possible. Then, just sum up the numbers to see how much the project will cost you as a whole.
Cost forecasing is about looking into potential trends, opportunities, and risks. You need to perform a risk-based cost analysis. Evaluate potential loss due to a delay in the supply of essential production materials, some technical issues, or even the dismissal of a very important employee. Choose anything that makes sense in your situation and add the predicted cost of the event to other estimation results.
Whereas regular cost estimation allows you to see if the planned project activities are financially feasible and optimize them accordingly, risk-based cost assessment shows how much money you need to use as a cushion against unpredictable and costly events.
Get free risk assesement templates here. 👈
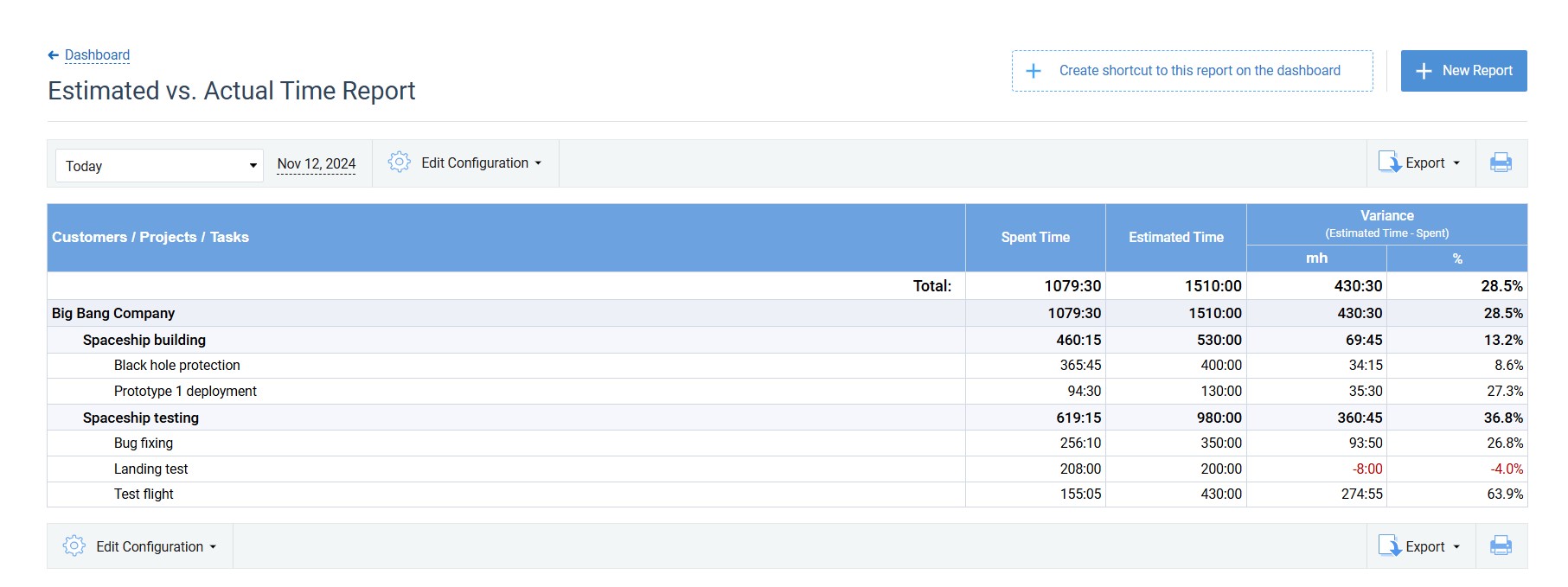
actiTIME reports provide a wealth of invaluable data to inform your project estimation process: from detailed hour tracking results to staff-related expenses and billable time per task. Apply this historical information in analogous cost estimation to enhance resource management in your future work.
Budgeting
A budget is a summary of all expenditures and/or revenues involved in the project. It states the final cost estimates, clarifies how much money you will have at different stages in the project’s life cycle, and indicates how much funds could and should be allocated to certain project activities.
In the end, a well-developed project budget serves as the foundation for cost control that your team must perform to avoid excess spending and get more profit.
There are several ways to approach your project budgeting process:
Incremental project budgeting means you use time estimates or historical time tracking data from previous projects to estimate your project costs and set budgets.
Activity-based budgeting starts by identifying your ideal revenues. Taking from there, you estimate how much work must be done to achieve the desired financial goal, estimate how much money you should put into that work, and create your budget using those estimates.
Value-based budgeting requires you to prioritize budget items based on their value for your project or business as a whole. In other words, you need to identify the resources and activities that are absolutely essential to your project and financial goals and eliminate the insignificant ones from your budget – only the important stuff remains.
Zero-based budgeting requires you to allocate budget based on the criteria of necessity and efficiency. “Management starts from scratch and develops a budget that only includes operations and expenses essential to running the business; there are no expenses that are automatically added to the budget” (CFI).
Speed up your budgeting process with our free project budget templates. 👇
Cost Control
Cost control is all about identifying, monitoring, and evaluating project costs in order to reduce expenses and maximize the revenues of a business. It is carried out by comparing the actual financial performance of the project with expectations stated in the budget.
In an ideal situation, your team should always comply with budget estimates. However, since cost overruns are frequent and are difficult to control 100% of the time, it is important to ensure that all expenses are properly recorded and, consequently, subjected to a thorough analysis.
By comparing data on actual project costs with those stated in the budget, managers can detect flaws in their approach to project cost management and disclose factors that were left without appropriate attention but require consideration. In this way, it becomes possible to enhance the accuracy and quality of cost management and improve the financial performance of future projects.
Here is a list of major procedures involved in cost control:
Cost tracking, i.e., the systematic monitoring of ongoing project expenses. This essential project cost management activity helps to collect important performance data and identify the risk of cost overruns early on. To attain better results, it’s vital to do it every single day of your work on a project. Luckily, you don’t have to track project costs manually – there are myriads of automated cost tracking software tools on the web. Check out actiTIME as an example.
Next, we have budget variance analysis, i.e., the comparison of your actual cost of work performed (ACWP) to the budgeted cost of work scheduled (BCWS). To perform this analysis, use the following simple formula:
Although cost control is never painless, by approaching it systematically and attentively, you will increase the chance of the project’s success to a substantial degree.
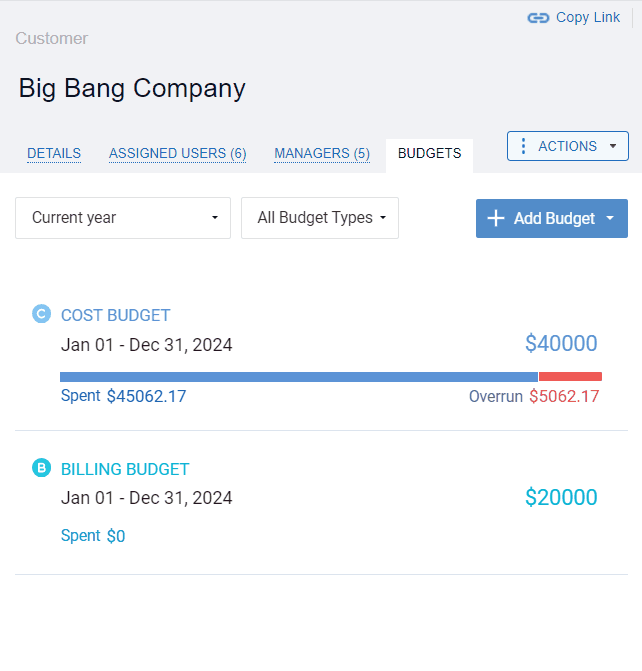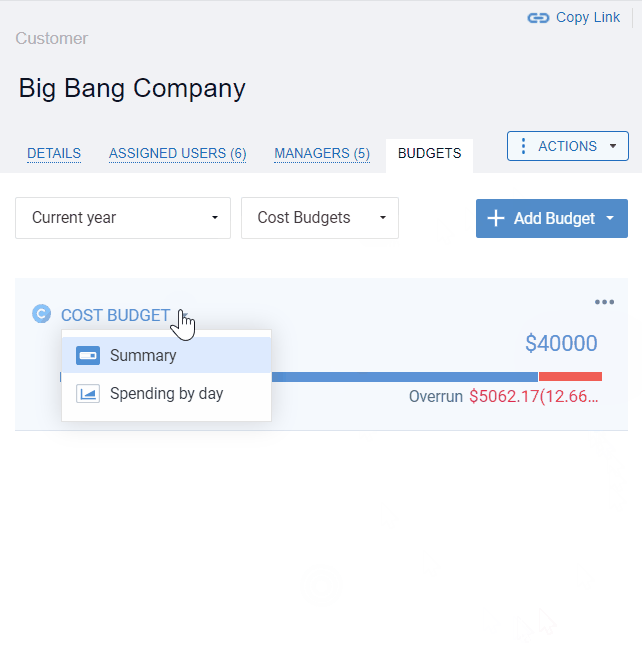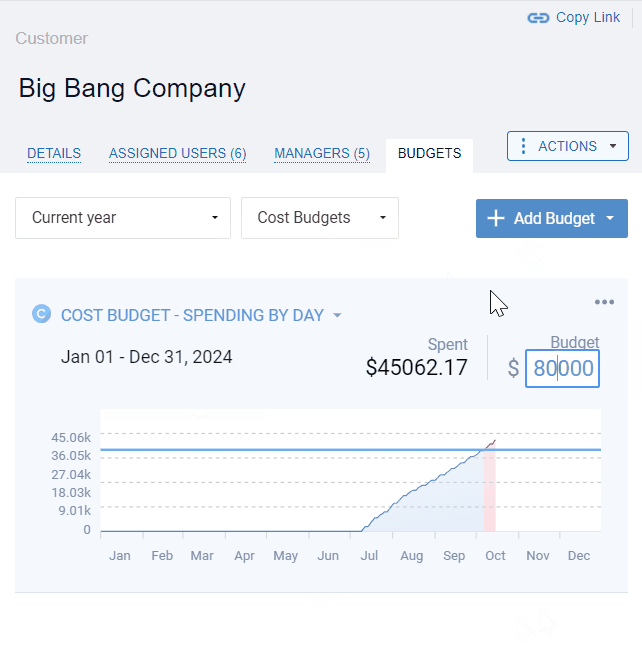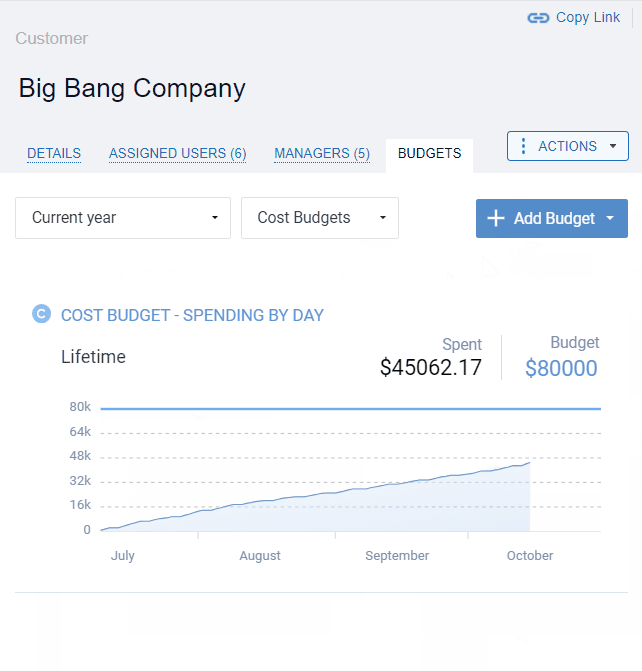
actiTIME’s visual budget tracker is the ultimate tool for cost control! It highlights budget overruns in red and lets you analyze the collected progress data as an overall summary of the entire budgeting period or a detailed breakdown by day.
Streamline Project Cost Management with actiTIME
To improve your project cost management outcomes and track project budgets with ease, consider adopting actiTIME. This multifunctional software solution has all you need to track performance costs, manage project budgets, and analyze data in depth.
Start by planning out your entire project scope: set deadlines and priorities for tasks, share other important details via comments, and allocate work to employees. Then, use detailed historical data from time and money reports to get more accurate cost and time estimates and analyze your financial performance at the end of the project.
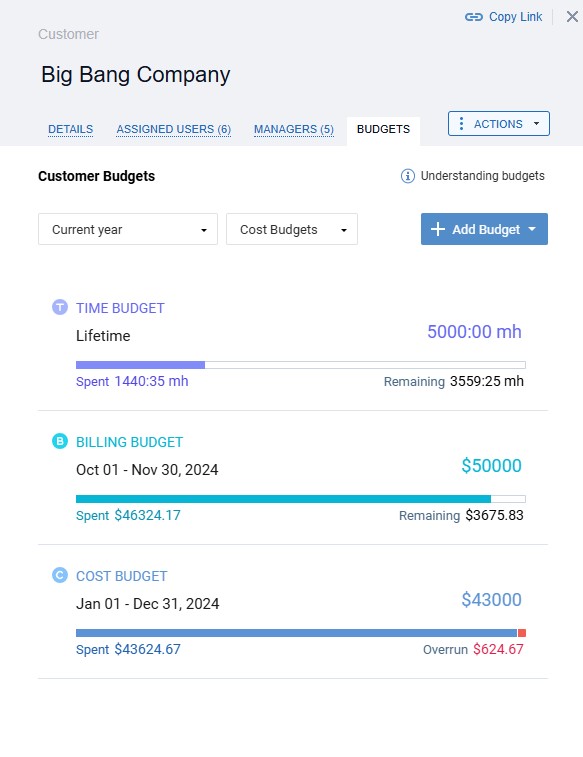
You can also set different types of budgets for entire projects and customers or individual tasks in actiTIME! Each budget comes with a visual progress bar that makes it super easy to monitor the use of resources over time and promptly address the risk of project overruns.
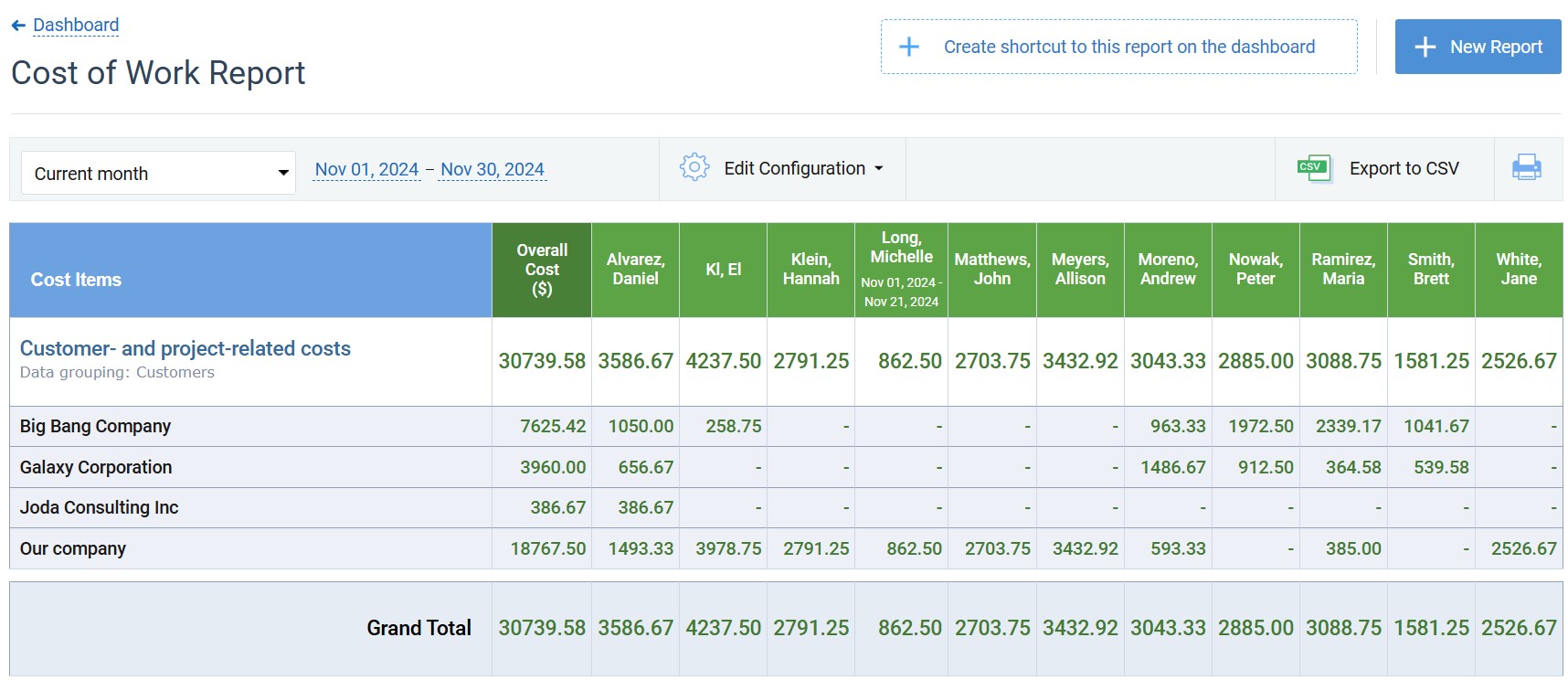
On top of that, actiTIME offers a variety of progress tracking tools to monitor project costs and other resources: visual estimate and budget trackers, multiple charts and reports, real-time widgets, Kanban board, and more!
Explore all these handy actiTIME features firsthand during a free 30-day trial.

















































