Emotions play a significant role in shaping our interactions and decision-making processes. When emotions are managed effectively, it can lead to better communication, reduced conflict, and enhanced teamwork.
Negative emotions at work, on the other hand, produce a lot of problems. In this post, we’ll explore them in detail and give you some tips on managing emotions at work effectively – both at the individual and the organization-wide level.
How Negative Emotions Affect Employees
Negative emotions at work can significantly impact an employee’s overall well-being and productivity. Here are some common ways in which these emotions can affect individuals:
- Decreased job satisfaction: Experiencing negative emotions can lead to a decline in job satisfaction, making work less enjoyable and fulfilling.
- Reduced motivation: Negative emotions can dampen motivation and make it difficult to stay engaged in tasks.
- Impaired performance: Stress, anger, or frustration can hinder an employee’s ability to perform their duties effectively.
- Increased absenteeism: Negative emotions may contribute to increased absenteeism due to illness, stress-related issues, or simply a lack of motivation.
- Conflict with coworkers: Unmanaged negative emotions can lead to interpersonal conflicts and strained relationships with colleagues.
- Burnout: Chronic exposure to negative emotions can contribute to burnout, a state of emotional exhaustion, and detachment from work.
- Physical health problems: Negative emotions can have a detrimental impact on physical health, leading to issues, such as headaches, digestive problems, and weakened immune systems.
The Effects of Negative Emotions on the Workplace
Negative emotions can also have a significant impact on the overall health and productivity of a workplace. Here are some of the effects:
- Decreased morale: When employees experience negative emotions, it can lead to a decline in morale throughout the organization. This can create a negative and unwelcoming atmosphere.
- Reduced productivity: Negative emotions can impair employees’ ability to concentrate, make decisions, and work effectively. This can lead to decreased productivity and efficiency.
- Increased turnover: Employees who are unhappy or stressed may be more likely to seek employment elsewhere. High turnover rates can be costly and disruptive to a company’s operations.
- Conflict and tension: Unmanaged negative emotions can lead to interpersonal conflicts, tension, and a toxic work environment. This can negatively impact teamwork and collaboration.
- Damage to reputation: A workplace with a negative atmosphere can damage a company’s reputation. This can make it difficult to attract and retain top talent.
- Financial losses: Negative emotions can lead to decreased productivity, increased turnover, and damage to reputation, all of which can have a negative impact on a company’s financial performance.
Common Causes of Negative Emotions at Work
Negative emotions at work can arise from various factors:
- Stressful workload: Excessive workload, tight deadlines, and high expectations can lead to stress, anxiety, and frustration.
- Unrealistic expectations: When employees are expected to perform beyond their capabilities or are given conflicting goals, it can lead to feelings of inadequacy and disappointment.
- Poor communication: Misunderstandings, lack of clarity, and ineffective communication can create confusion, frustration, and resentment.
- Negative work environment: A toxic work environment characterized by bullying, harassment, or discrimination can contribute to negative emotions.
- Lack of job security: Concerns about job security, layoffs, or promotions can create anxiety and stress.
- Work-life imbalance: Difficulty in balancing work and personal commitments can lead to stress, guilt, and burnout.
- Unresolved conflicts: Unresolved conflicts with colleagues or supervisors can create tension and resentment.
- Lack of recognition or appreciation: Feeling undervalued or unappreciated can lead to feelings of dissatisfaction and demotivation.
- Personality clashes: Incompatible personalities or working styles can create friction and tension.
- Personal issues: Personal problems outside of work can spill over and impact emotional well-being at the workplace.
Managing Emotions at Work: Tips for Employees
One of the keys to managing emotions at work as an individual is through developing emotional intelligence (EI) – the ability to understand, manage, and utilize emotions effectively.
It involves self-awareness, self-regulation, social awareness, and relationship management:
Self-awareness
Self-awareness is the ability to recognize and understand your own emotions, thoughts, and behaviors.
Here’s how to develop and use self-awareness in the workplace:
- Pay attention to your emotions: Notice how you feel in different situations. Are you feeling stressed, happy, frustrated, or something else? Understanding your emotional responses can help you identify triggers and manage them more effectively.
- Keep a journal: Writing down your thoughts and feelings can help you identify patterns and gain a better understanding of your emotional responses.
- Reflect on your behavior: Consider how your emotions influence your behavior at work. Do you tend to become defensive when criticized? Do you procrastinate when feeling overwhelmed? Understanding these connections can help you manage your emotions more effectively.
- Identify your values: Understanding your core values can help you make decisions that align with your beliefs and avoid situations that cause emotional distress.
- Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness involves being present in the moment and observing your thoughts and feelings without judgment. This can help you become more aware of your emotional state and its impact on your behavior.
Self-regulation
Self-regulation is the ability to control your impulses and reactions, particularly in response to emotions. It enables you to manage stress, resolve conflicts, and maintain positive relationships.
Here’s how to develop and use self-regulation in the workplace:
- Take deep breaths: Deep breathing can help calm your nervous system and reduce stress. When you feel overwhelmed, take a few deep breaths to help regulate your emotions.
- Count to ten: Give yourself a moment to pause and count to ten before responding to a stressful situation. This can help prevent impulsive reactions and allow you to think more rationally.
- Challenge negative thoughts: When you find yourself thinking negatively, challenge those thoughts and replace them with more positive ones. This can help you manage stress and improve your mood.
- Practice assertiveness: Assertiveness involves expressing your needs and feelings in a clear and respectful manner. This can help you avoid passive-aggressive behavior and resolve conflicts more effectively.
- Set boundaries: Establishing healthy boundaries can help you protect yourself from negative influences and avoid situations that trigger emotional outbursts.
- Learn to say no: It’s important to be able to say no to requests that are unreasonable or that you don’t have the time or energy for. This can help you avoid feeling overwhelmed and stressed.
- Seek support: Talking to a trusted friend, mentor, or therapist can help you manage stress and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
Social awareness
Social awareness is the ability to recognize and understand the emotions, thoughts, and perspectives of others. It helps you build strong relationships, resolve conflicts, and collaborate effectively.
Here’s how to develop and use social awareness in the workplace:
- Active listening: Pay attention to what others are saying, both verbally and nonverbally. Show that you’re engaged by maintaining eye contact, nodding, and asking questions.
- Empathy: Put yourself in others’ shoes and try to understand their feelings and perspectives. This can help you respond to their needs and concerns in a compassionate and supportive way.
- Observe nonverbal cues: Pay attention to people’s body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. These cues can provide valuable information about their emotions and thoughts.
- Ask open-ended questions: Instead of asking yes or no questions, ask open-ended questions that encourage others to share their thoughts and feelings.
- Avoid assumptions: Don’t make assumptions about others’ intentions or feelings. Instead, ask them directly to clarify their meaning.
- Respect diversity: Be mindful of cultural differences and avoid making stereotypes. Treat everyone with respect and dignity.
- Recognize group dynamics: Pay attention to the dynamics within your team or department. Understanding how people interact can help you navigate social situations more effectively.
- Build relationships: Take the time to get to know your colleagues on a personal level. This can help you build trust and rapport, which is essential for effective collaboration
Relationship management
Relationship management is the ability to build, maintain, and nurture relationships with others. It’s key to effective collaboration and a positive work environment.
Here’s how to develop and use relationship management in the workplace:
- Effective communication: Communicate clearly and openly with your colleagues. Avoid misunderstandings by expressing your thoughts and feelings in a direct and respectful manner.
- Conflict resolution: Approach conflicts with a positive and constructive attitude. Use active listening, empathy, and compromise to find mutually beneficial solutions.
- Teamwork: Collaborate effectively with your team members to achieve shared goals. Encourage teamwork, support each other, and celebrate successes together.
- Build trust: Trust is essential for building strong relationships. Be reliable, honest, and transparent in your interactions with others.
- Provide feedback: Give and receive feedback constructively. Offer positive feedback to encourage and motivate others, and be open to feedback yourself.
- Manage disagreements: When disagreements arise, approach them calmly and respectfully. Avoid blaming or attacking others.
- Celebrate successes: Recognize and celebrate the achievements of your colleagues. This can help boost morale and strengthen team bonds.
- Network: Build relationships with people outside your immediate team or department. Networking can provide opportunities for career advancement and personal growth.
Self-reflection checklist
- What recent situations at work have triggered negative emotions for me?
- How do I typically respond when I feel stressed or upset at work?
- Are there specific people at work who consistently affect my mood negatively? Why?
- How do I communicate my feelings when I’m upset at work?
- What are my physical symptoms when experiencing negative emotions at work?
- Do I tend to keep my feelings to myself, or do I share them with colleagues or supervisors?
- How does my work environment contribute to my emotional state?
- What coping mechanisms do I usually resort to when feeling negative emotions at work?
- How do I unwind or relax after a challenging day at work?
- Can I identify patterns in my negative emotional responses?
- How do I balance my work life and personal life to ensure emotional well-being?
- Have I set realistic expectations for myself at work?
- What strategies can I use to remain calm in high-pressure situations?
- How do I manage my workload to prevent feelings of overwhelm?
- How frequently do I reflect on my workday to understand my emotional triggers?
- What role does feedback from colleagues or supervisors play in my emotional responses?
- Do I practice any mindfulness or stress-reduction techniques during the workday?
- How comfortable am I in asking for help when feeling overwhelmed?
- Do I take regular breaks to recharge during my workday?
- How well do I manage time to reduce work-related stress?
- What steps can I take to create a supportive network at work?
- How do I ensure I am in a positive and productive mindset each morning before work?
- What are my favorite activities outside of work that help improve my mood?
- How can I be more proactive in addressing workplace conflicts?
- How well do I set boundaries to protect my emotional health at work?
- How do I celebrate small victories to boost my morale?
- How effective am I at unplugging from work during off-hours?
- What are three things I am grateful for at work today?
- How can I improve my emotional resilience in the workplace?
- What resources or support systems are available to help me manage negative emotions at work?
Managing Emotions at Work: Tips for Employers
Creating a comfortable work environment is essential for employee satisfaction, productivity, and retention.
Here’s what you can do as an employer to help your team members feel more at ease and avoid negative emotions:
Physical comfort
- Ergonomic workstations: Ensure that workstations are designed to promote good posture and reduce physical discomfort.
- Temperature control: Allow employees to adjust their individual workspaces to their preferred temperature.
- Noise reduction: Implement measures to reduce noise levels, such as soundproofing or noise-canceling headphones.
- Lighting: Provide adequate lighting to prevent eye strain and fatigue.
Emotional comfort
- Open communication: Foster a culture of open and honest communication where employees feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and concerns.
- Supportive environment: Create a supportive and inclusive environment where employees feel valued and respected.
- Work-life balance: Encourage a healthy work-life balance by offering flexible work arrangements or providing resources for stress management.
- Employee recognition: Acknowledge and reward employees for their contributions to the company.
Social comfort
- Team-building activities: Organize team-building activities to foster camaraderie and improve relationships among employees.
- Social events: Host social events or gatherings to encourage employees to interact and socialize outside of work.
- Diversity and inclusion: Promote diversity and inclusion initiatives to create a welcoming and inclusive environment for all employees.
Psychological comfort
- Job security: Provide employees with a sense of job security and stability.
- Career development: Offer opportunities for professional growth and development, such as training programs or mentoring.
- Clear expectations: Clearly communicate expectations and goals to reduce uncertainty and anxiety.
Before Negative Emotions at Work Start to Build Up…
Employee performance and absence tracking can serve as valuable tools to identify when negative emotions are starting to impact team productivity. By closely monitoring these metrics, you can detect early warning signs and take proactive steps to address the underlying issues.
Key indicators to watch:
- Decreased performance: A decline in overall productivity, quality of work, or meeting deadlines can be a sign that employees are feeling overwhelmed, stressed, or demotivated.
- Increased errors and missed deadlines: A rise in mistakes or errors in work can indicate that employees are distracted, fatigued, or experiencing difficulties with concentration.
- Frequent absences: Unexplained or excessive absences can be a sign that employees are struggling with stress, burnout, or personal issues.
Pro tip:
actiTIME offers intuitive time tracking functionality that helps you identify employees who are falling behind schedule or spending more time on tasks than anticipated. This can highlight potential bottlenecks or problems with productivity.
On top of that, actiTIME lets you track overtime hours to identify teams or individuals who are consistently working beyond their regular hours. And with time off tracking functionality, you can spot if someone is absent too frequently and then take action to address the problems.
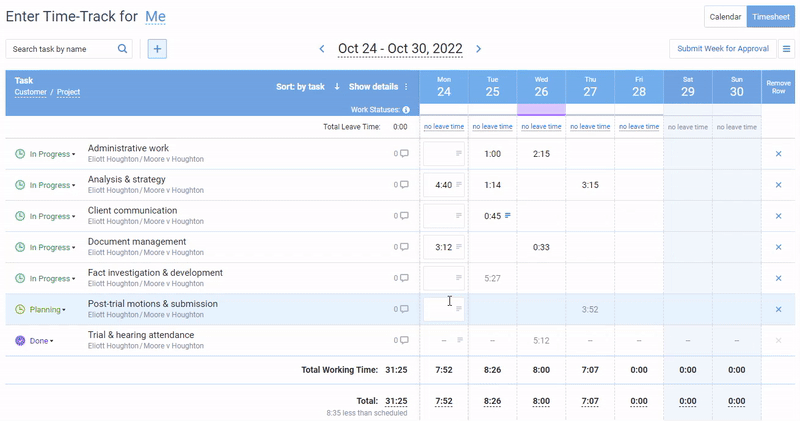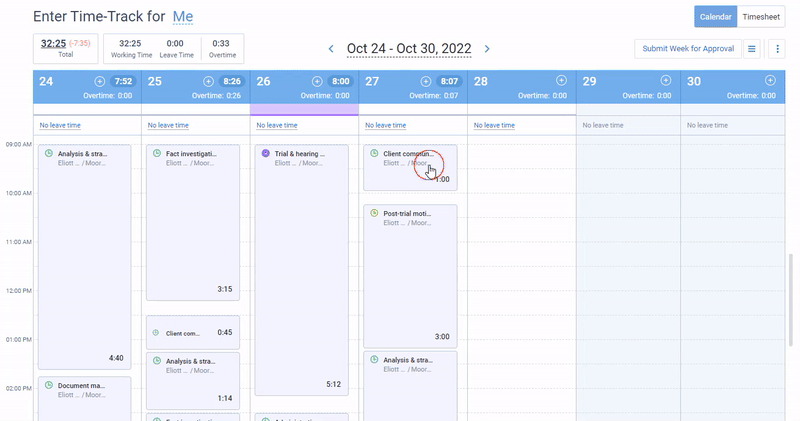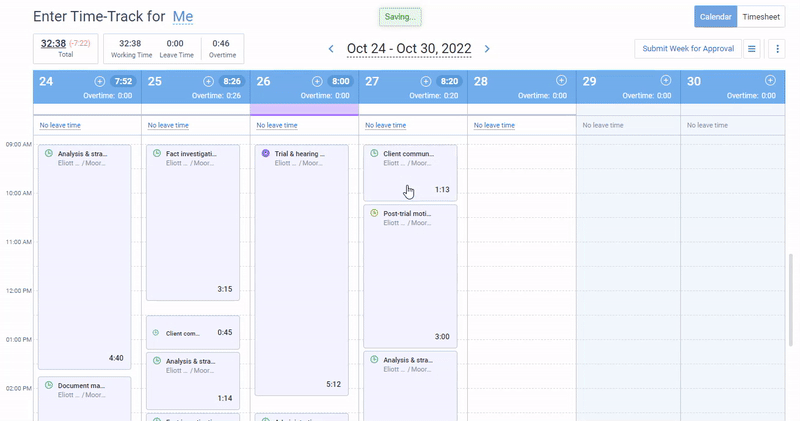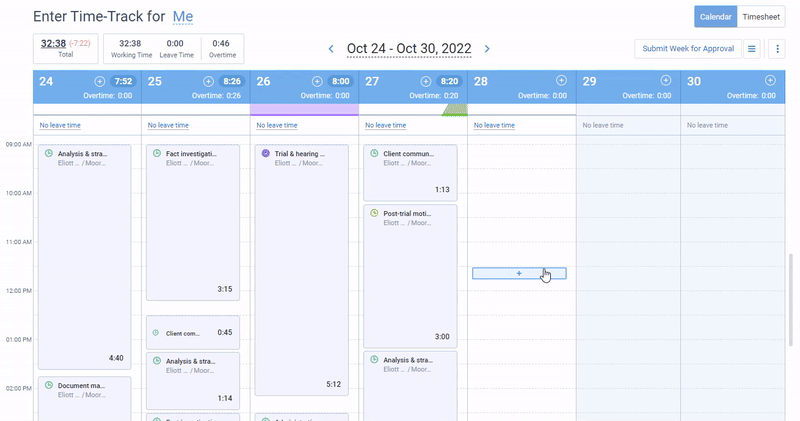
Analyzing the data:
- Correlations: Look for correlations between changes in performance, absence rates, and other metrics with potential triggers for negative emotions, such as workload, deadlines, or changes in the organization.
- Patterns: Identify patterns or trends that suggest a buildup of negative emotions over time. For example, a gradual decline in performance or an increase in absences may indicate a developing issue.
- Individual and team analysis: Analyze both individual and team-level data to identify specific areas of concern and potential solutions.
Pro tip:
actiTIME features a handful of team performance reports that let you analyze the use of resources over time and compare your initial estimates with actual results.
Besides, you can integrate it with actiPLANS, a flexible resource scheduling solution, to get access to comprehensive leave reports and analyze data on staff absence and attendance.
Sign up for a free actiTIME trial to track employee performance consistently and get profound insights on team dynamics and productivity – this is a solid starting point in managing emotions at work effectively.