Have you ever found yourself deep in thought about the complexities of employee pay rates, wondering how to navigate the intricate web of wages, salary negotiations, and compensation packages?
In the hustle and bustle of today’s corporate world, understanding pay rates is crucial for both employers and employees.
Whether you’re trying to decode your paycheck or decide how much to offer a new hire, this article is here to break down the conversation around cash in a way that’s straightforward and engaging.
So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s dive into the dollars and cents of it all.
What Is Pay Rate?
A pay rate is the amount of money you earn for each hour of work. It’s that simple. Whether you flip burgers, design websites, or crunch numbers, your pay rate determines how much cash you bring home at the end of the day.
Intriguingly, it’s not just about the dollars and cents – it’s also a reflection of your skills, experience, and even the demand for your profession.
Companies usually base pay rates on industry standards to ensure they’re competitive, but they can also offer more if an employee has some unique talent or experience that stands out.
3 Primary Types of Pay Rates
Regular Pay Rate
This is the most common type of pay rate. Your regular pay rate is what you earn per hour during your standard work hours.
For example, if you’re making $20 an hour and you work 40 hours a week, your paycheck for that week would be $800 before taxes and deductions.
Think of it as your bread and butter – the dependable part of your pay that you can always count on.
Overtime Pay Rate
Overtime pay kicks in when you work more than your standard hours, usually over 40 hours in a week.
In many places, this is calculated at 1.5 times your regular pay rate. So, if your regular rate is $20 an hour, your overtime rate would be $30 an hour.
For instance, if you worked an extra 10 hours this week, you’d earn an additional $300 just for those extra hours. It’s a nice little bonus for putting in the extra time.
Time Off Rate
Then there’s the time off rate, which is what you earn while you’re not working, like during vacation days or sick leave.
Often, this is paid at your regular pay rate. So, if you take a day off and your regular rate is $20 an hour, you’d still earn $160 for that 8-hour day as if you were working.
It’s the way companies ensure you still get paid while you’re recharging your batteries or taking care of yourself.
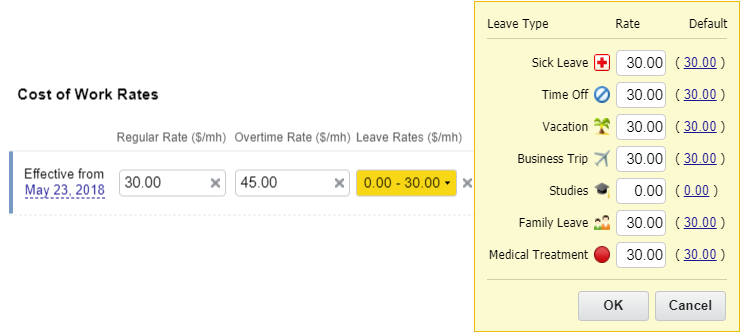
Use actiTIME to set different types of pay rates for your entire team or individual employees and track staff-related costs based on each hour of regular work, overtime, or leave time.
Pay Rate vs. Bill Rate
Pay rate and bill rate are not the same thing, though they’re closely related.
The pay rate is the amount of money that an employee takes home as their salary or wages. On the flip side, the bill rate is what a company charges a client for that employee’s work.
Let’s break it down with some clear examples.
Imagine you’re a software developer. Your pay rate might be $50 an hour, meaning that’s what you see hit your bank account after a day’s work. However, your company bills clients $150 an hour for your time and expertise.
Why the big difference?
Well, that extra $100 covers a range of business costs like company overhead, benefits, taxes, equipment, and hopefully, some profit too!
Think of it like eating at a fancy restaurant versus cooking at home. At home, you might spend $10 on ingredients for a tasty meal (your pay rate), but at a restaurant, that same meal could cost $30 (the bill rate). That extra $20 covers the chef’s skill, the ambiance, utilities, staff wages, and of course, a little profit for the restaurant.
To sum things up, while the pay rate is an employee’s personal earnings, the bill rate factors in all those hidden costs and is crucial for keeping a business running smoothly. Understanding this distinction gives better insights into how businesses operate and how one person’s skills contribute to the broader economic picture.
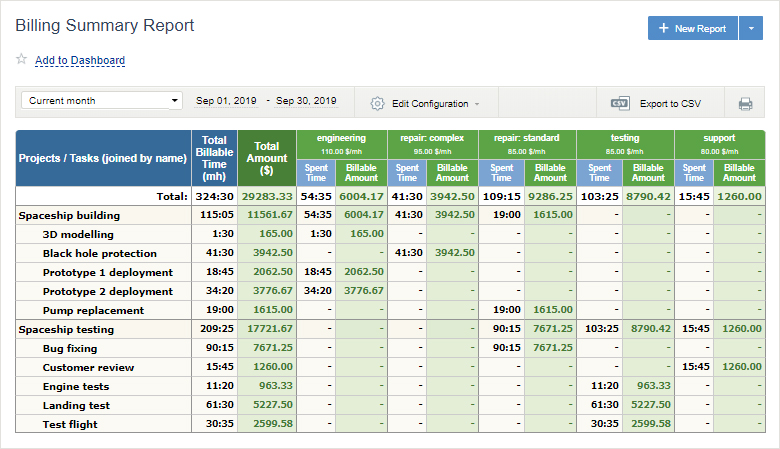
Set billing rates for different types of work in actiTIME to easily keep tabs on project revenues per hour invested in work.
How to Define Your Employees’ Pay Rates: Factors to Consider
1. Market rate
The market rate is essentially the current pay rate for a particular job within a specific industry or geographical area. It’s a benchmark against which pay rates are measured.
To determine the market rate, you need to look at what similar companies are offering for comparable roles. This involves doing a bit of research: surveying salary data, looking at job listings, and maybe even talking to other professionals in the industry.
For example, imagine you’re hiring a software developer in San Francisco. The tech industry there is booming, so you’d expect the market rate to be higher compared to a smaller city where the demand for tech jobs isn’t as intense.
The salary for an entry-level software engineer at a big tech company versus a small startup will be different as well. At a large company like Google, the market rate might be around $100,000 a year, while a startup might offer $80,000. Both are gauging the market rate but also factoring in what they can afford and what additional perks they might offer (like stock options or flexible work hours).
2. Experience and education
Experience and education comprise a valuable combo of knowledge and skills that someone brings to the table:
- A person who’s been in the field for 10 years is likely to have a treasure trove of practical know-how that a newbie just doesn’t have. Plus, seasoned pros have probably faced and tackled a slew of different scenarios, making them more adept and agile in their roles.
- Education, on the other hand, sets the foundation. While anyone can learn on the job, having a formal education often means the basics and theories are already in the bag.
Let’s say you’re hiring a marketing manager. Candidate A has a bachelor’s degree in marketing and has spent the last five years working for a well-known brand, developing winning campaigns that boosted sales by 20%. Candidate B has a high school diploma but has somehow managed to carve out three years within a startup, learning the ropes through sheer grit and creativity.
While both are valuable, Candidate A’s formal education and extensive experience are reasonably worth a higher pay rate because they bring a tested and proven track record.
So, you should be ready to reward that hefty mix of hands-on experience and hard-earned education if you want to keep a highly skilled and talented employee on your team.
3. Company budget
A budget is the financial blueprint of your organization. It’s a comprehensive plan that outlines where your money comes from and where it needs to go.
For example, a startup that has just received a solid chunk of funding needs to allocate funds wisely – covering everything from office rent and equipment to marketing and, most importantly, salaries. If you splurge too much on high salaries without a solid revenue stream, you might run out of cash before your product even sees the light of day.
On the flip side, let’s say you work for a well-established corporation with a stable income. Here, the budget might allow for more competitive salaries, perhaps even bonuses and perks. Yet, even large companies have financial constraints and priorities – investing too heavily in one department’s salaries might mean cutting back on others.
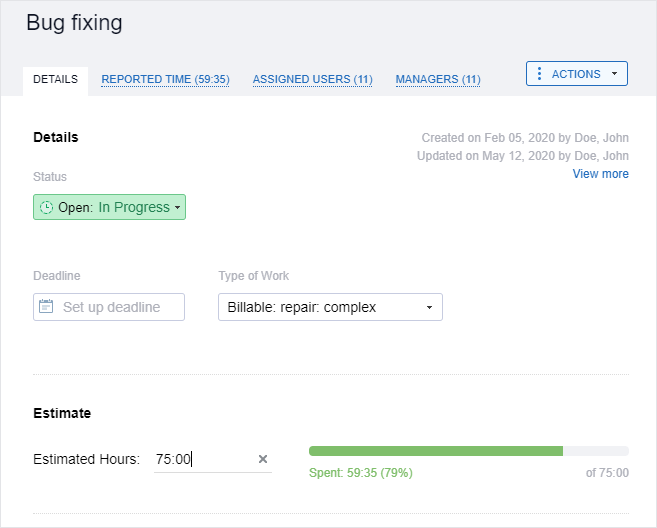
Use actiTIME to set work estimates and automated notifications on budget overruns to stay in control of your business costs.
4. Job complexity
Job complexity is all about how intricate and demanding a role is within an organization. It’s not just about the tasks an employee performs, but also the level of expertise required, the range of skills applied, and the degree of problem-solving needed on a day-to-day basis.
Think about a software developer versus a data entry clerk:
- The developer is likely dealing with complex coding, system troubleshooting, and perhaps even leading a team of junior developers.
- In contrast, the data entry clerk might be responsible for inputting information into databases, which, while crucial, doesn’t usually call for the same level of analytical thinking or creativity.
Thus, two of these jobs will be paid differently.
5. Employee performance
Employee performance is a metric that shows how well an employee carries out their job responsibilities and contributes to the company’s goals. High-performance employees often go above and beyond their basic duties, demonstrating initiative, problem-solving skills, and a strong work ethic.
For example, a sales associate who consistently meets and exceeds their monthly targets will drive revenue and secure client satisfaction. Their performance not only highlights their effectiveness but also positively impacts the company’s bottom line.
When employees perform at a high level, they should be rewarded accordingly. This not only promotes a culture of excellence but also motivates other team members to elevate their performance.
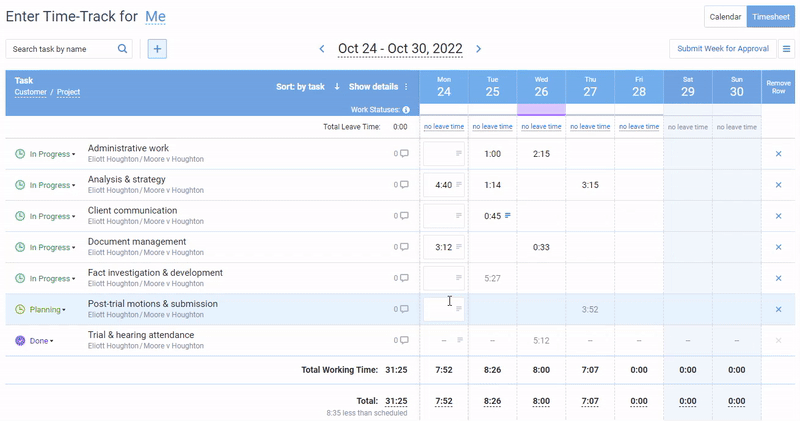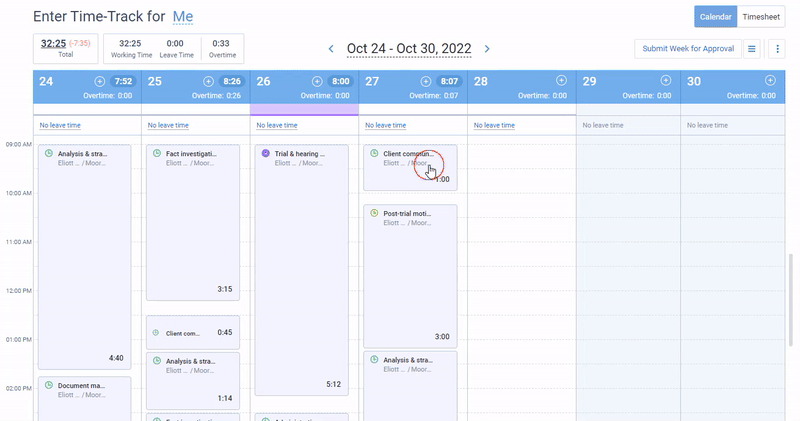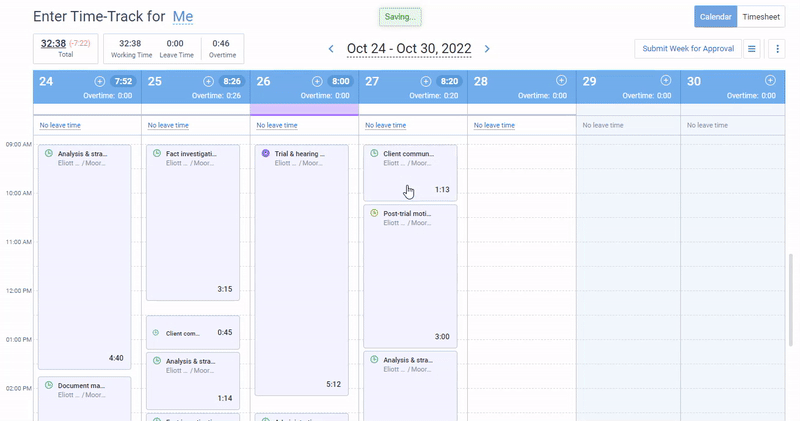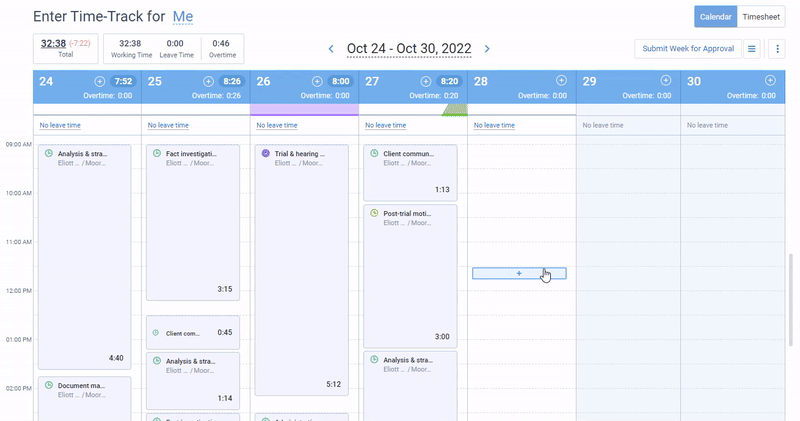
Track work hours and task progress with actiTIME to identify employees who never fail to meet the set deadlines and high performance standards.
6. Economic conditions
Simply put, when the economy is booming and companies are thriving, they’re more likely to offer higher salaries to attract and retain top talent. Conversely, during economic downturns or recessions, companies might tighten their belts and limit pay raises or even implement salary cuts.
For example, during the global financial crisis of 2008, many industries saw a significant slowdown, which led to widespread job losses and salary freezes.
On the flip side, in recent years, the tech industry has experienced rapid growth and fierce competition for skilled workers, driving up salaries and offering generous compensation packages to entice top talent.
This is easy to see in places like Silicon Valley, where tech giants like Google and Apple are known for their hefty paychecks and attractive benefits.
7. Benefits package
Employee benefits are like the cherry on top of your compensation sundae. It’s not just about the paycheck as such but about everything else that sweetens the deal.
A good benefits package covers a whole range of goodies – from health insurance and retirement plans to paid time off (PTO) and company perks, which play a crucial role in attracting and retaining top talent.
For instance, offering comprehensive health insurance can significantly reduce out-of-pocket expenses for employees, giving them peace of mind. Retirement benefits, like 401(k) matching, are also a big draw – who doesn’t love the idea of building a nest egg with a little help from their employer?
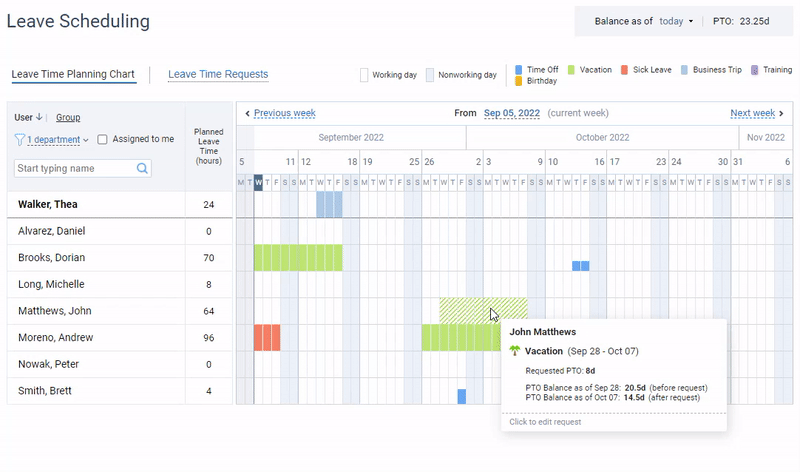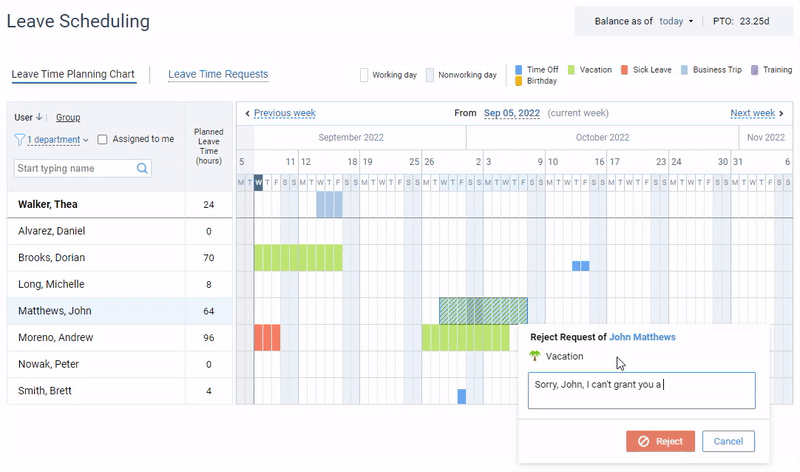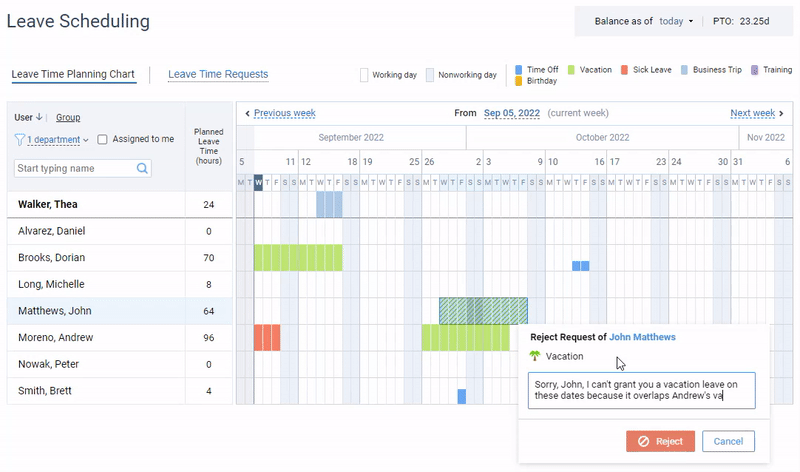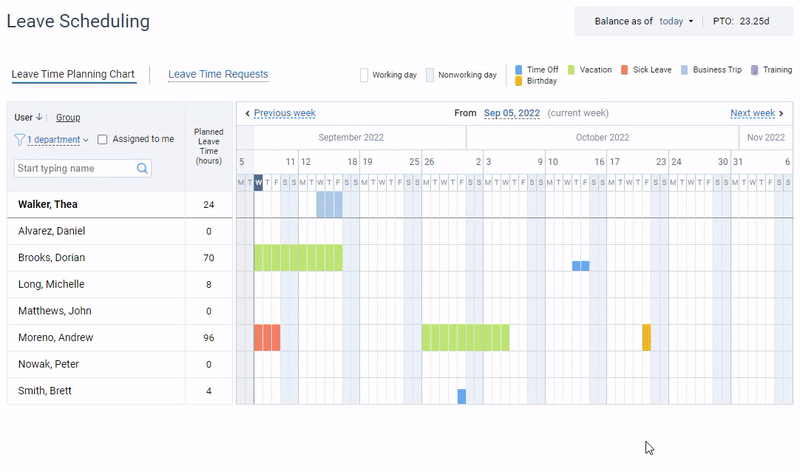
Attract top talent with a generous PTO policy and track days off the easy way with actiPLANS.
8. Legal requirements
Governments set laws to protect employees from unfair wages and ensure everyone gets a fair shake. Hence, it’s vital to make sure you’re playing by the rules when it comes to paying your team
For instance, there’s the minimum wage law. In the United States, the federal minimum wage is currently $7.25 per hour, but individual states can set their own rates, which sometimes are much higher. New York, for example, has a minimum wage of $15-16 per hour. Employers need to stay updated with these laws because they can change.
Another important legal requirement is overtime pay. According to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), non-exempt employees must receive overtime pay at a rate of one and a half times their regular rate for hours worked over 40 in a workweek. This means if your regular wage is $10 per hour, your overtime pay must be $15 per hour.
And let’s not forget equal pay laws. Employers can’t pay someone less just because of their gender, race, or other protected characteristics. The Equal Pay Act mandates that men and women will receive equal pay for equal work.
Pay Rate Calculation Examples
For employees
Pay rate calculations for employees are usually straightforward – just start with their annual salary and break it down.
For example, if Jenny gets $52,000 a year, you can find her weekly pay by dividing $52,000 by the 52 weeks in a year. That means Jenny makes $1,000 a week.
If she works the standard 40 hours a week, divide that $1,000 by 40, and voila! Jenny’s hourly rate is $25.
For freelancers
Freelancers are a different ball game because they often charge by the project or by the hour, and there’s no fixed annual salary.
Let’s say John is a freelance graphic designer who charges $60 an hour. If he lands a project that will take 30 hours based on his estimation, you just multiply that rate by the hours – $60 x 30 – which totals $1,800 for the project.
But what if John wants to set a project rate instead of an hourly rate?
He should estimate how long it’ll take to complete the project and multiply his hourly rate by that time. If John thinks a website design will take about 50 hours, he can charge a flat fee of $3,000 ($60/hour x 50 hours).
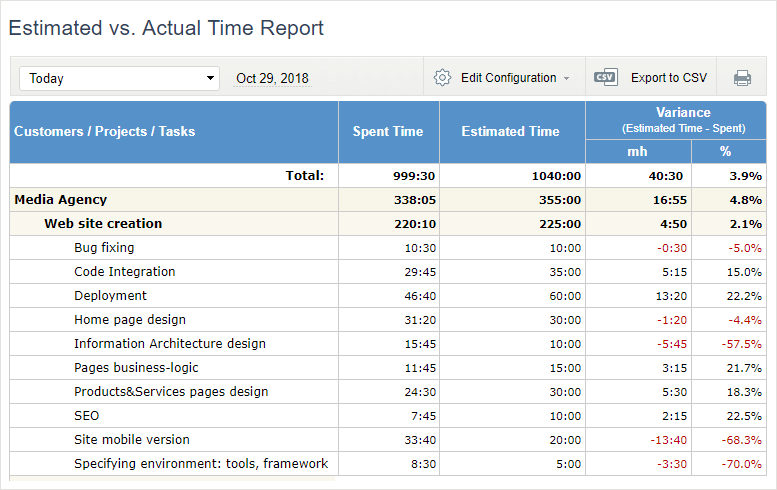
Collect accurate time tracking data with the help of actiTIME and use it to estimate and rate your projects correctly.
Why It’s Vital to Set Pay Rates Correctly
- Attracting top talent. The job market is competitive, and offering attractive pay rates is crucial to luring the best candidates. Talented professionals know their worth and are likely to choose positions that compensate them fairly. If your pay rates are below market standard, you might miss out on some robust additions to your team.
- Boosting morale and productivity. Fair compensation isn’t just about the paychecks. It’s about valuing employees’ contributions. When employees are paid what they deserve, their morale and productivity tend to skyrocket. They feel appreciated, motivated, and more committed to delivering their best work.
- Legal compliance and avoiding penalties. Incorrect pay rates can lead to costly legal issues. By ensuring your rates comply with labor laws and regulations, you safeguard your business against potential fines and lawsuits. This not only protects your finances but also your brand’s reputation.
- Maintaining competitive pricing. If your pay rates are too high, you’ll need to charge more for your products or services just to keep up. This can make you less competitive in the market, pushing potential customers towards your competitors who can offer similar quality at lower prices. Keep your pay rates balanced to maintain a competitive edge.
Balance Your Pay Rates to Maximize Financial Gains
Looking for a simple way to streamline various facets of your workforce management, including employee pay? actiTIME is here to save the day!
Not only can you establish individual pay rates, but you can also factor in variables like overtime and time off. This ensures that every paycheck is both accurate and transparent.
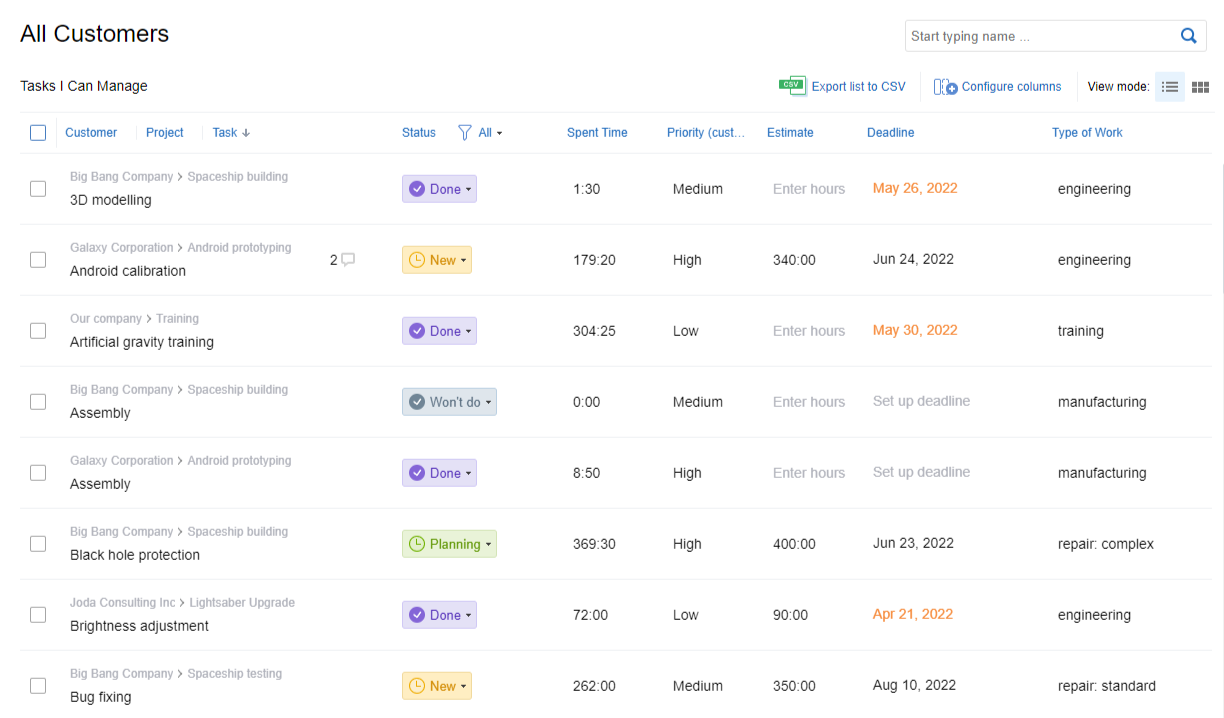
Tracking team performance? actiTIME’s got you covered.
The software allows you to monitor individual and team productivity in real time, so you can spot bottlenecks and celebrate excellence effortlessly.
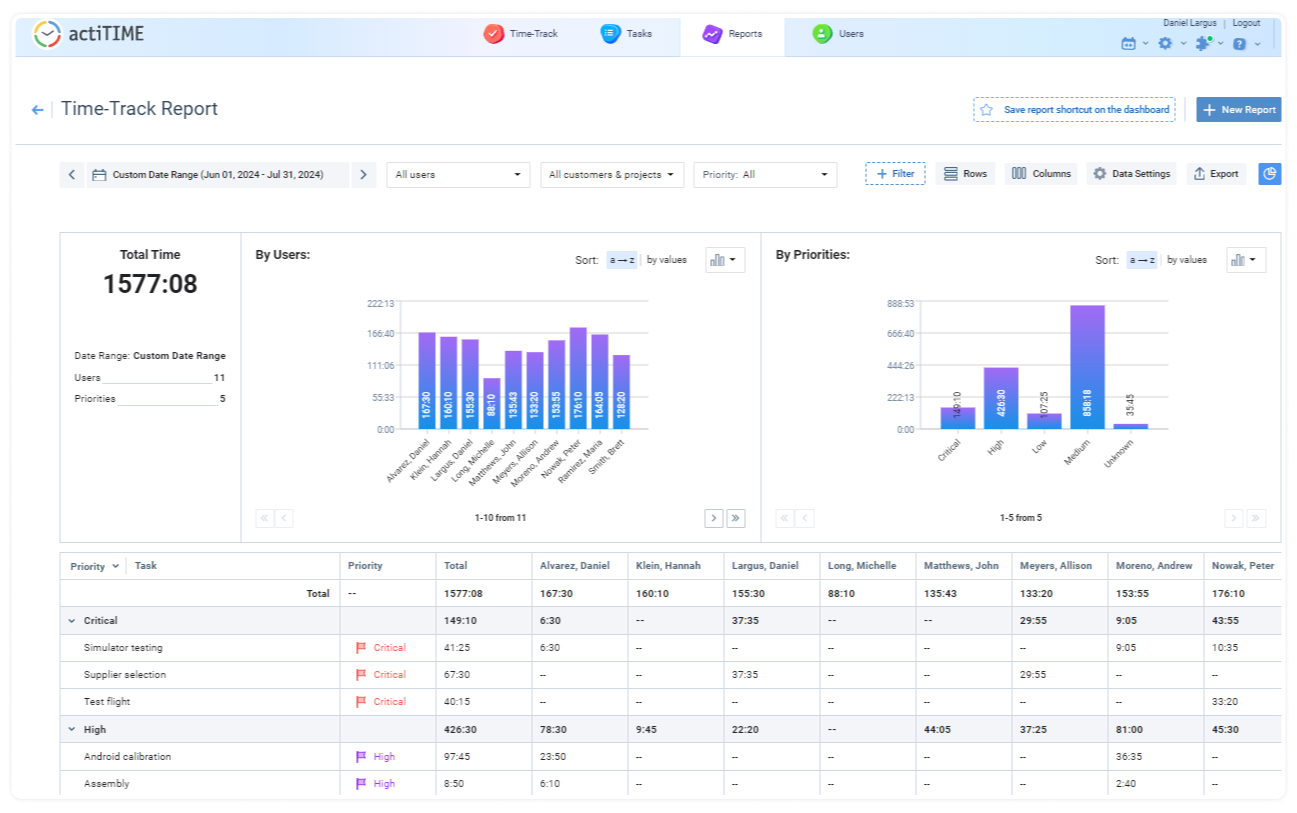
Need to keep tabs on staff-related costs and project revenues? actiTIME takes care of that too.
By providing detailed reports, you can see exactly where your money is going and how much each project is earning – this turns budget management into a walk in the park.
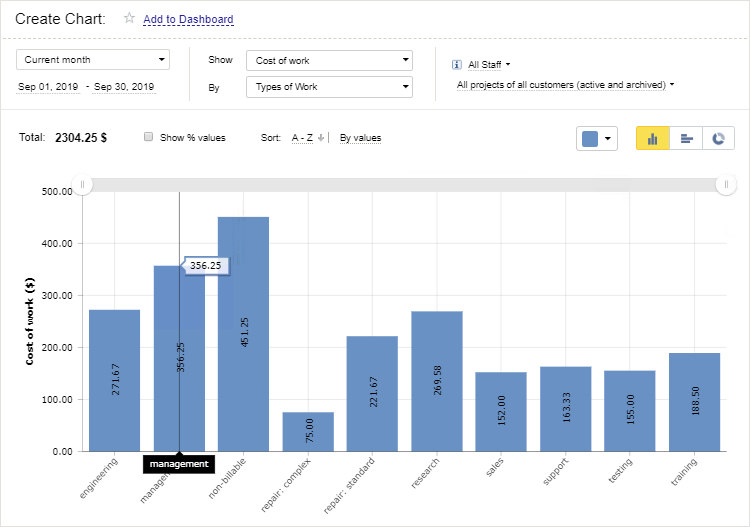
When it comes to analyzing financial data by the hour of work, actiTIME shines.
You can drill down into your financials with incredible precision, analyzing staff-related costs and project revenues on an hourly basis. This granular level of detail helps you make informed decisions, optimize schedules, and ultimately, improve your bottom line.
In short, actiTIME turns the complex world of employee management and financial analysis into something as easy as pie. So, sign up for a free trial and give it a go!

















































